An exhibition room of "Techniques in Observing Nature" in Japan Gallery
The National Museum of Nature and Science covers five research fields: Zoology, Botany, Earth Science, Anthropology, and Science and Engineering. Items on exhibit range from materials related to a variety of flora and fauna, to the history of science and technology as well as the engineering filed. The Edo shogunate built an astronomical facility in the area that is now Taito City, which reflects that facilities and people, related to science, have a long history of coming together. In 1949, the museum's name was changed from "Tokyo Science Museum" to "National Science Museum," and Takenoshin Nakai, who was a prominent botanist and a father of literary scholar Hideo Nakai, a scholar of literature, was appointed as its director general.
In the Japan Gallery, items in a variety of fields, including the natural history in Japan, the history of technology, and science and engineering, are exhibited under the theme of "The Environment on the Japanese Islands" The building has three floors of exhibition rooms. On the first floor, south wing, which is themed "Techniques in Observing Nature" materials and instruments from the Edo Period are exhibited in four sections: "Sky -- celestial globe and astronomy," "Earth -- seismometer," "Time -- clock" and "Microscopic world -- microscope."
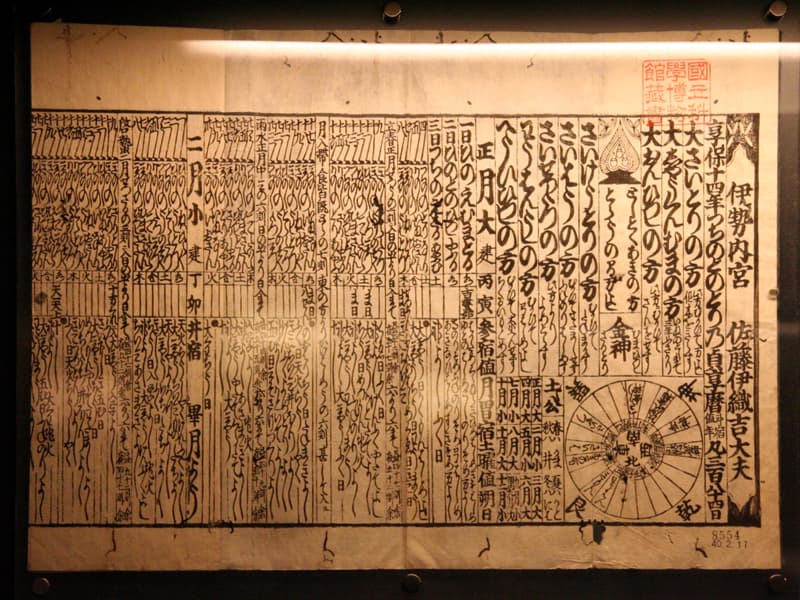
This is the first Japanese lunisolar calendar, which was compiled by Harumi Shibukawa, an astronomical calendar scholar in the early Edo Period. Jokyo-Calendar, also called "Yamato-Calendar," had been used from 1685 to 1755, the year when a calendar reform took place. In recognition of his achievement, Shibukawa was appointed as the first astronomical member of the personal in the Edo shogunate government.

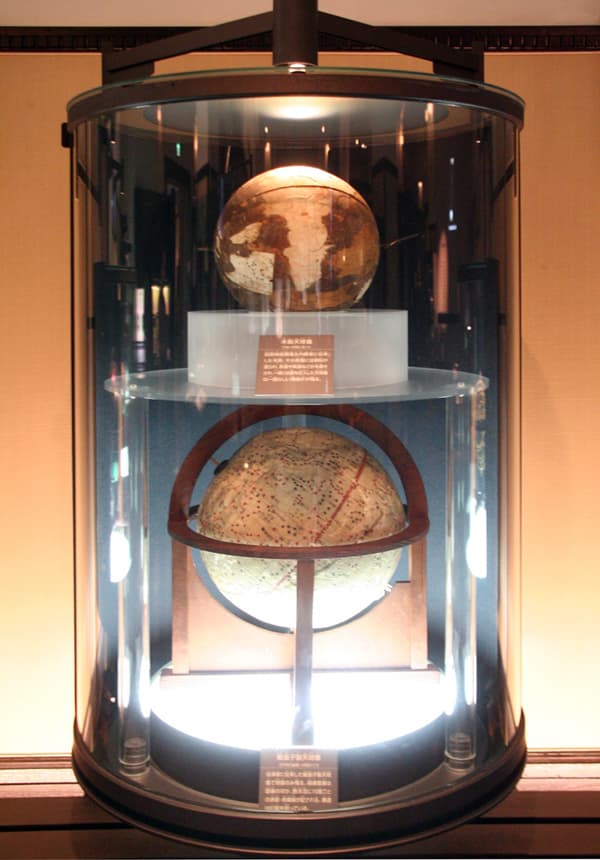
Celestial Globe made of wood(above, around 1786)
This wooden sphere was brought to the Naito family who was the lord of the Nobeoka domain. Powdered calcium carbonate was applied to the surface And then the equator and ecliptic was drawn by a writing brush.
This paper celestial globe was brought to the Yatsu family. Only the sphere remains. The longitude and latitude lines are drawn in the Western style, which draws right ascension/declination every 10 degrees as well as diagonal. The ecliptic is drawn incorrectly.

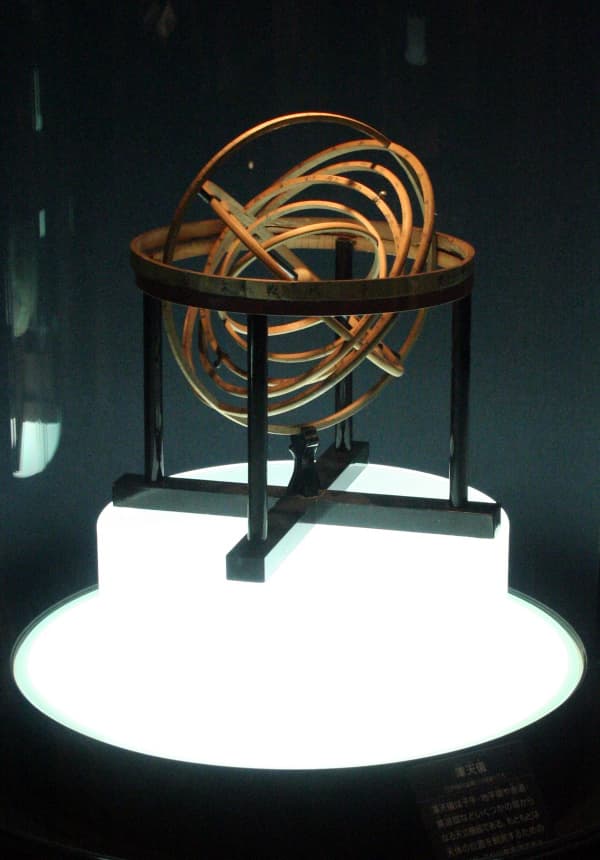
An armillary sphere is an astronomical instrument which consists of several rings, including the horizon/meridian ring and the equatorial/ecliptic ring. It was originally used for observing positions of celestial objects, but this is an educational armillary sphere.



On the roof of the Japan Gallery, there is an old-style astronomical observatory that is still in active service. There are two iron plates placed at the entrance, the inscriptions read as Twenty centimeters equatorial telescope, designed, manufactured and set up by NIPPON KOGAKU K.K. (abbreviation), completed in October 1931" and "Equatorial telescope room, donated by Chiyomatsu Nakamura from Mito City." There are also some scribbles that looks like childrens’ writing scratched on the surface of its outside wall, the characters include names and some old dates such as "Showa 21" and "1950."


On the roof of the Japan Gallery, there is an old-style astronomical observatory that is still in active service. There are two iron plates placed at the entrance, the inscriptions read as Twenty centimeters equatorial telescope, designed, manufactured and set up by NIPPON KOGAKU K.K. (abbreviation), completed in October 1931" and "Equatorial telescope room, donated by Chiyomatsu Nakamura from Mito City." There are also some scribbles that looks like childrens’ writing scratched on the surface of its outside wall, the characters include names and some old dates such as "Showa 21" and "1950."